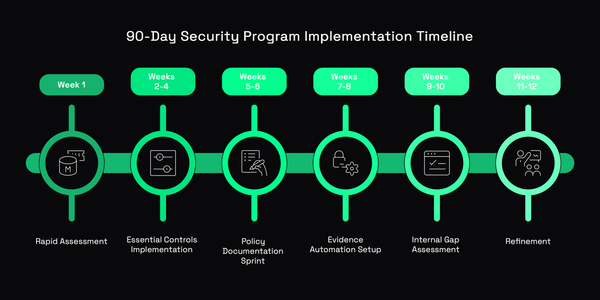
How CIOs & CISOs Can Automate Security Processes

Nikoloz Kokhreidze
Discover how automation of security processes empowers organizations to respond swiftly to cyber threats. Learn benefits and best practices for CIOs and CISOs.

Organizations of all sizes are increasingly vulnerable to cyber-attacks, data breaches, and other unexpected events. To protect their data and systems, they must be able to respond quickly to these types of incidents. To do this, organizations must have a strong security posture, which includes the ability to deploy automated security processes. This article is a primer for CIOs and CISOs who want to understand how automation of security processes can positively impact their organizations.
What is Automation of Security Processes?
Automation of security processes is using technology and software to automate specific security tasks. Automation can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of security operations by automating repetitive, manual processes, such as patch management, vulnerability scanning, and access control. It can also help organizations respond quickly to unexpected events by providing automated alerting and response capabilities.
Examples of automation of security processes include:
- Automated monitoring and alerting: Use security software to automatically monitor potential threats and alert security teams when a possible incident is detected.
- Automated incident response: Use security automation software to automatically respond to security incidents, such as quarantining infected devices or blocking malicious IP addresses.
- Automated compliance management: Use security software to track compliance with security standards and regulations, such as HIPAA, PCI-DSS or SOC2.
- Automated vulnerability management: Use security software to automatically scan for vulnerabilities in systems and networks and patch them as soon as possible.
- Automated security testing: Use security software to test systems and applications for vulnerabilities and security weaknesses automatically.
Benefits of Automating Security Processes
Automating security processes has several key benefits for organizations. On a high-level, it can help organizations save time and money by reducing the manual labor required to perform security tasks. Automation can also help improve the accuracy and consistency of security operations, as it eliminates the potential for human error. Additionally, automation can help organizations respond quickly to unexpected events, as these events can trigger automated processes in response to a security incident.
To go into more detail, organizations investing in automation will notice the following benefits:
- Increased efficiency: Automation can streamline security operations, reduce the time and resources required to complete security tasks, and improve overall security performance.
- Improved accuracy: Automated security processes can reduce the risk of human error, ensuring that security tasks are completed consistently and accurately.
- Increased scalability: Automation can help organizations to scale their security operations as their business grows, allowing them to handle an increasing volume of security tasks.
- Better threat detection: Automated security processes can help detect potential threats more quickly and accurately, allowing organizations to respond more effectively to security incidents.
- Improved compliance: Automated security processes can help organizations to maintain compliance with security standards and regulations more efficiently, reducing the risk of penalties and fines.
- Increased security: Automating security processes can help organizations to improve their overall security posture, reducing the risk of security incidents and breaches.
Is Security Blocking Your Next Enterprise Deal?
Let's discuss how fractional CISO services can unlock your pipeline without the full-time overhead.
Critical Requirements for Starting Working with Automation
While automating tasks can sound attractive, the effort required to get there should not be underestimated. Organizations looking in this direction must be prepared to invest significant resources.
Implementing automation requires a combination of different resources, including:
- Deep knowledge of the organization: The first thing organizations should consider when implementing automation is their knowledge about the areas they would like to automate. This can include the organization's culture, processes, policies and regulatory or compliance requirements. Suppose organizations do not have this laid out at the beginning of the process. In that case, they might have difficulty assessing if the automation is making the correct decisions.
- Security engineering teams: Organizations will need dedicated security engineering teams to design, implement, and maintain automated security processes. These teams should have a mix of skills, including security expertise, programming and scripting, and experience with security automation tools.
- Solutions and tools: Organizations will need to invest in solutions and tools that support the automation of security processes. This can include security automation software, security orchestration and automation platforms, and security analytics tools.
- Skills: Organizations will need to develop the necessary skills to support the automation of security processes. This includes programming and scripting, as well as an understanding of security concepts and best practices.
- Data and infrastructure: Automated security processes will require access to the necessary data and infrastructure to operate effectively, such as logs and network traffic data. This should be collected, stored and made accessible to the tools and solutions that will be used for automating the processes.
- Processes and procedures: Organizations will need to have transparent processes and procedures in place to ensure that automated security tasks are executed correctly and that the right actions are taken in response to alerts and incidents.
- Integration: Organizations must ensure that automated security processes are integrated with existing security solutions and tools, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and security incident and event management systems.
Best Practices for Automating Security Processes
There are several best practices that organizations can follow when automating security processes:
- Start with a clear goal: Before automating any security process, organizations should clearly understand what they hope to achieve. This will help to ensure that the automation is aligned with the organization's overall security strategy and objectives.
- Identify critical processes for automation: Organizations should focus on automating processes that are repetitive, time-consuming, or error-prone, as these are likely to provide the most significant benefits from automation.
- Prioritise automation projects: Organizations should prioritize automation projects based on the potential impact on the organization's security posture and the resources required to implement them.
- Test and validate automation: Organizations should test and validate automated security processes before deploying them in production to ensure that they function correctly and provide the expected results.
- Monitor and evaluate automation: Organizations should monitor and assess the performance of automated security processes over time to ensure that they continue to meet the organization's security needs.
- Continuously update and improve: Automated security processes need continuous improvement; organizations should regularly review and update the processes and tools used for automation and consider new techniques, technologies and trends in the security field.
By following these best practices, organizations can effectively automate security processes, improve their overall security posture and reduce the risk of security incidents and breaches.
Conclusion
Organizations of all sizes must be able to respond quickly to unexpected events to protect their data and systems. They also should be able to reduce the workload coming from repetitive tasks. Automation of security processes can help organizations achieve this goal by automating repetitive, manual processes and providing automated alerting and response capabilities. By following best practices for automating security processes, organizations can ensure that their automation tools are up-to-date, properly configured, and integrated with other security tools. This will help ensure that automated processes are efficient and effective, enabling organizations to respond quickly and effectively to unexpected events.