What Microsoft Knows About AI Security That Most CISOs Don't?

Nikoloz Kokhreidze
Traditional security fails with AI systems. Discover Microsoft's RAI Maturity Model and practical steps to advance from Level 1 to Level 5 in AI security governance.
When I first read Microsoft's Responsible AI Maturity Model (RAI MM) I got to view a road to AI maturity from a very different perspective. It not only shaped my understanding of AI governance, it also immensely motivated me to learn the leadership strategies for it, so much so that I immediately signed up for Standford's Building an AI-Enabled Organization program.
RAI MM offers a comprehensive framework that security leaders can leverage to assess and enhance their organization's approach to AI governance. But it's not just another compliance checkbox - it's a strategic tool that can transform how your organization builds, deploys, and secures AI systems.
In this article, I'll break down the RAI Maturity Model and show you exactly how to use it to:
- Identify critical gaps in your AI governance structure
- Build cross-functional collaboration that actually works
- Develop practical strategies for implementing responsible AI practices
- Create a roadmap for maturing your organization's AI security posture
Let's dive in.
Is Security Blocking Your Next Enterprise Deal?
Let's discuss how fractional CISO services can unlock your pipeline without the full-time overhead.
Why Traditional Security Frameworks Fall Short for AI
Most security leaders I speak with are trying to retrofit existing security frameworks to address AI risks. This approach is fundamentally flawed.
AI systems present unique challenges that traditional security models weren't designed to address:
- They can fail in unpredictable ways that evade standard testing
- They require cross-functional expertise that security teams often lack
- They create new privacy concerns through training data memorization
- They introduce novel attack vectors like prompt injection and model poisoning
The RAI Maturity Model addresses these gaps by providing a structured approach to assessing and improving your organization's AI governance capabilities.
The Three Pillars of the RAI Maturity Model
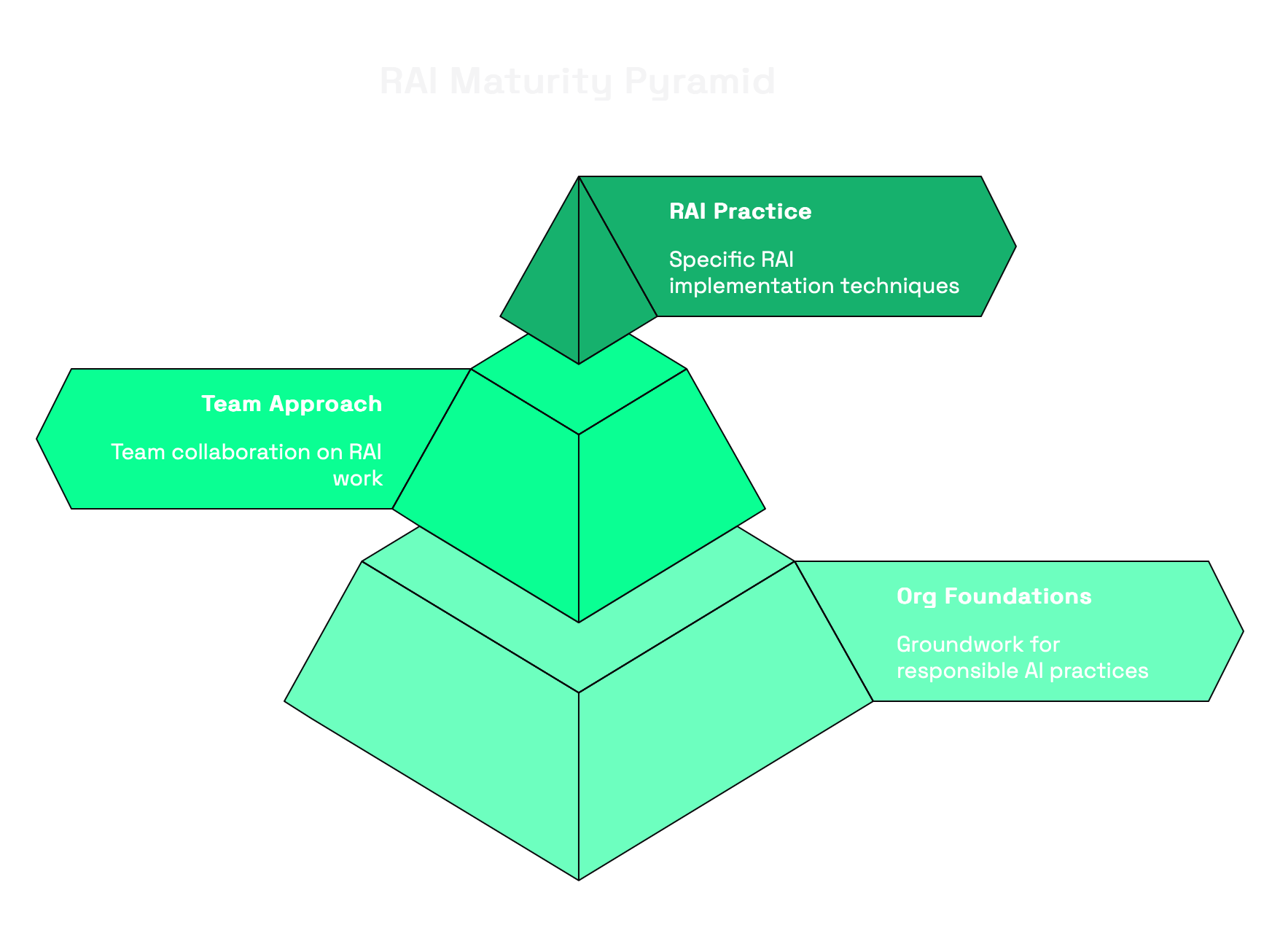
The RAI MM is organized into three interconnected categories:
1. Organizational Foundations
These dimensions establish the groundwork for responsible AI practices:
- Leadership and Culture
- Governance
- RAI Policy
- RAI Compliance Processes
- Knowledge Resources
- Tooling
2. Team Approach
These dimensions focus on how teams collaborate on RAI work:
- Teams Valuing RAI
- Timing of RAI in Development
- Motivation for AI Products
- Cross-Discipline Collaboration
- Sociotechnical Approach
3. RAI Practice
These dimensions address specific RAI implementation:
- Accountability
- Transparency
- Identifying, Measuring, Mitigating, and Monitoring RAI Risks
- AI Privacy and Security
Each dimension has five maturity levels, from Level 1 (Latent) to Level 5 (Leading). But here's the critical insight: progression between levels isn't linear. Moving from Level 1 to Level 2 often requires creating entirely new processes, while advancing from Level 3 to Level 4 might just involve formalizing existing practices.
Is Security Blocking Your Next Enterprise Deal?
Let's discuss how fractional CISO services can unlock your pipeline without the full-time overhead.
The Missing Link in Your Security Strategy
One of the most important things I found in the RAI MM is the AI Security dimension, which represents a critical blind spot for most cybersecurity professionals. This dimension I think deserves a special attention as it bridges traditional security practices with the unique challenges posed by AI systems.
Traditional security frameworks fall dangerously short when applied to AI systems. While most security leaders have processes and policies for addressing conventional threats, AI introduces novel attack vectors that require specialized approaches.
The RAI Maturity Model explicitly recognizes this gap through its AI Security dimension, which complements existing security frameworks by addressing AI-specific considerations such as model evasion, adversarial attacks, and other threats captured in frameworks like MITRE ATLAS.
The Dangerous Gap Between Traditional and AI Security
Most organizations exist in a precarious state where they've achieved reasonable maturity in conventional security but remain at Level 1 or 2 in AI security maturity. This creates a false sense of security that leaves AI systems vulnerable to sophisticated attacks.
At Level 1 maturity, teams understand general security risks but remain unaware of AI-specific threats. They might have robust traditional security practices but fail to recognize that AI systems can be compromised through entirely different vectors:
- Adversarial examples that cause misclassification
- Training data poisoning that subtly alters model behavior
- Model extraction attacks that steal proprietary algorithms
- Prompt injection attacks that manipulate generative AI outputs
By Level 3, teams recognize that AI security risks aren't automatically covered by existing security processes. They begin implementing specific mitigations and updating incident response processes to include adversarial attacks.
At Level 5, organizations integrate comprehensive adversarial testing and threat modeling into the AI development pipeline, conducting regular assessments when substantial changes are made to models.
Why Traditional Security Approaches Fail with AI
Traditionally we have been focusing on protecting systems with deterministic behavior. You secure an application by controlling inputs, managing authentication, encrypting data, and monitoring for known attack patterns.
But AI systems, differently. They are probabilistically. They:
- Learn patterns from training data that may contain hidden vulnerabilities
- Make decisions based on statistical inference rather than explicit programming
- Can be manipulated through subtle perturbations undetectable to humans
- May expose sensitive information through their outputs
These characteristics create fundamentally different attack surfaces that traditional security tools and methodologies aren't designed to address.
Practical Steps to Advance Your AI Security Maturity
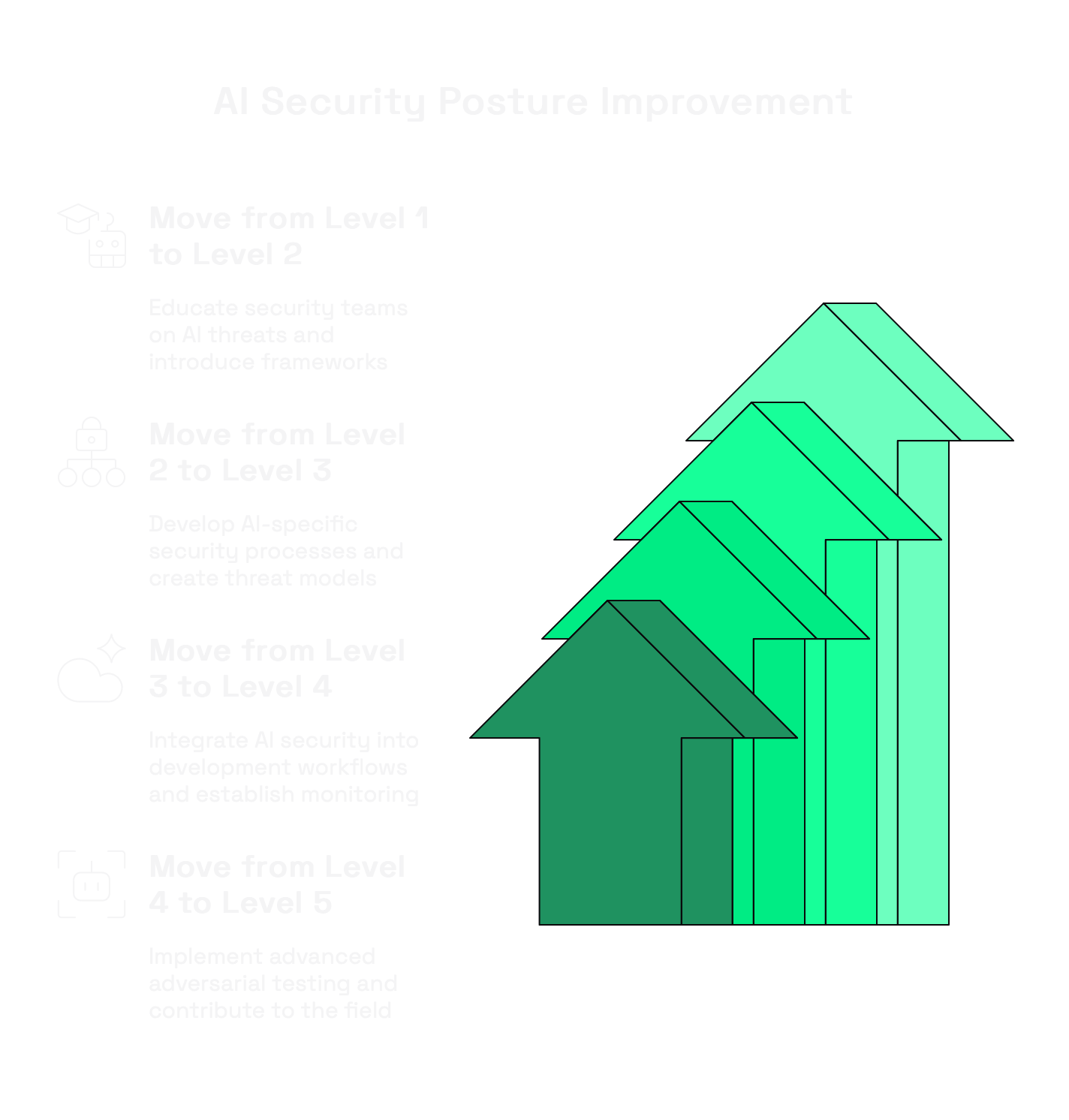
Based on the RAI Maturity Model, here's how you can systematically improve your AI security posture:
Moving from Level 1 to Level 2:
- Educate your security team on AI-specific threats
- Introduce frameworks like MITRE ATLAS to help teams understand the AI threat landscape
- Conduct workshops on adversarial machine learning concepts
- Partner with data science teams to understand your organization's AI systems
- Apply traditional methodologies as a starting point
- Extend your Security Development Lifecycle to include AI-specific considerations
- Begin documenting AI assets and their security requirements
- Identify which traditional security controls can be adapted for AI systems
Moving from Level 2 to Level 3:
- Develop AI-specific security processes
- Create threat models specifically for AI systems
- Update incident response procedures to include AI-specific attack scenarios
- Implement basic adversarial testing for critical AI models
- Build awareness of AI security posture
- Inventory all AI models in production
- Document model provenance and supply chain
- Identify which models have undergone security assessment
Moving from Level 3 to Level 4:
- Integrate AI security into development workflows
- Implement security gates for AI model deployment
- Develop automated testing for common adversarial attacks
- Create AI-specific security requirements for development teams
- Establish comprehensive monitoring
- Deploy monitoring for model drift and performance degradation
- Implement detection for potential adversarial inputs
- Create alerting for unexpected model behavior
Moving from Level 4 to Level 5:
- Implement advanced adversarial testing
- Conduct regular red team exercises against AI systems
- Use automated tools like Counterfit for comprehensive testing
- Develop custom attack scenarios based on your specific AI use cases
- Contribute to the field
- Share lessons learned with the broader security community
- Participate in standards development
- Contribute to open-source security tools for AI
The Security Leader's Guide to Implementing the RAI Maturity Model
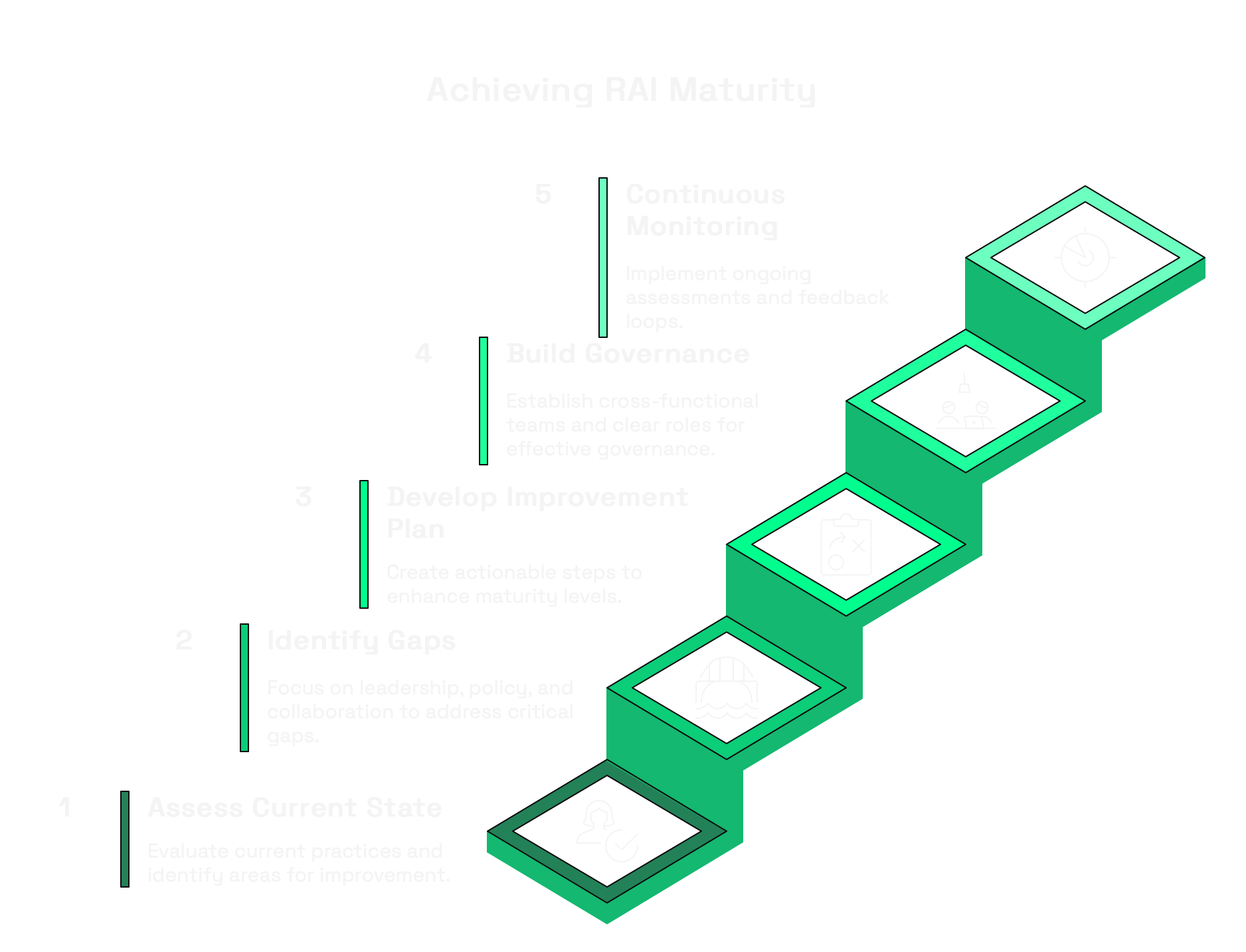
Ok, now that you know how to advance your AI security maturity, let me show you how to practically apply RAI Maturity Model.
Here's my step-by-step approach:
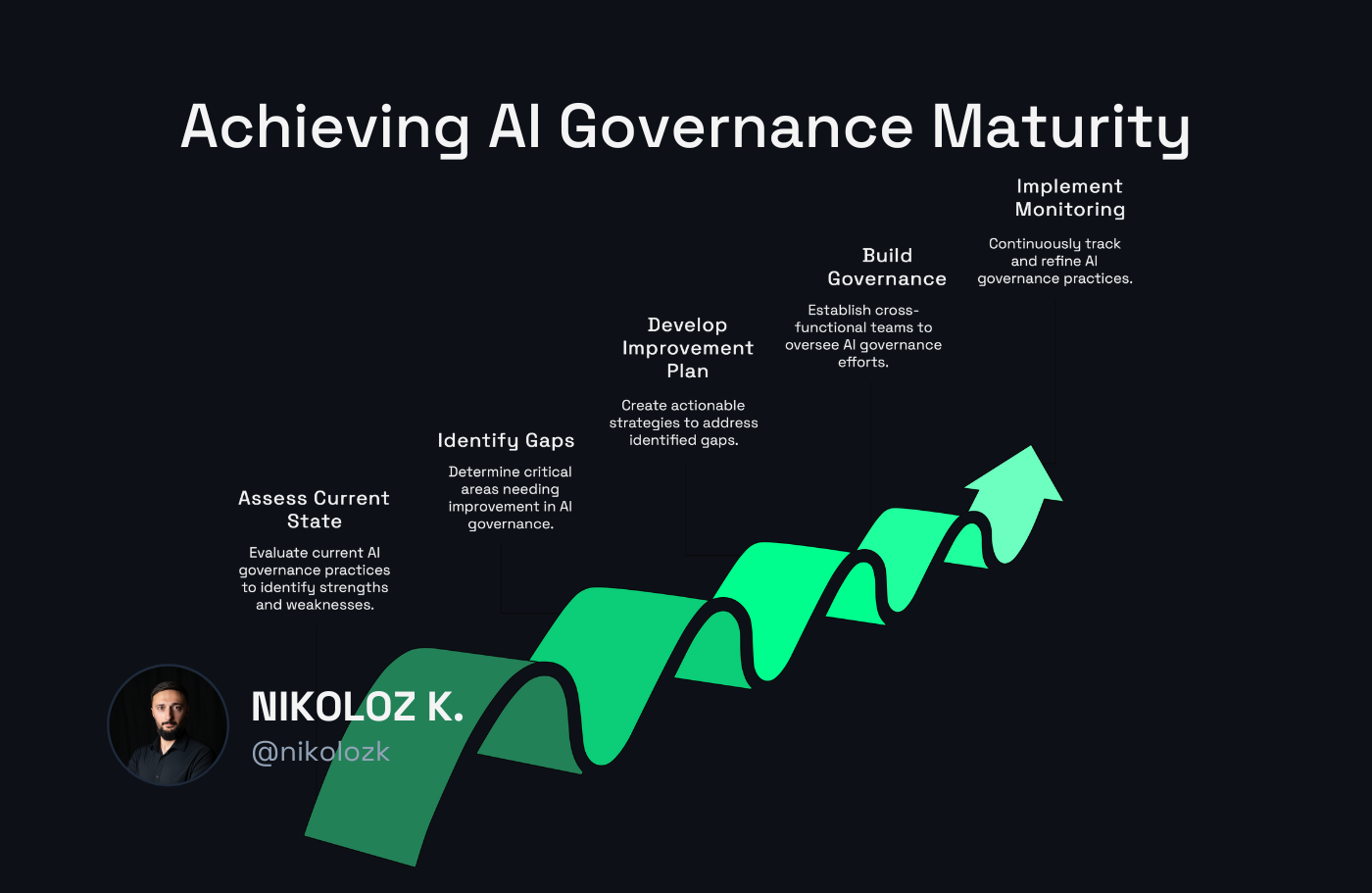
Step 1: Assess Your Current State
Start by evaluating where your organization stands on each dimension to identify specific areas for improvement.
For example, when assessing "AI Security," ask:
- Are we applying traditional security methodologies to AI systems?
- Do we have processes for addressing AI-specific security issues?
- Are we using AI-specific security frameworks like MITRE ATLAS?
- Is adversarial testing integrated into our development pipeline?
Be brutally honest in your assessment, after all you are doing this for your own benefit. I've seen too many organizations overestimate their maturity, only to be blindsided by incidents later.
Step 2: Identify Your Critical Gaps
Not all dimensions require equal attention. Focus on the foundational elements first:
- Leadership and Culture: Without executive buy-in and resource allocation, your RAI efforts will stall. If you're at Level 1 or 2 here, this should be your top priority.
- RAI Policy: A clear policy provides the framework for all other RAI activities. Without it, teams lack guidance on what "good" looks like.
- Cross-Discipline Collaboration: AI risks can't be addressed by security teams alone. If your organization scores low here, focus on building bridges with data science, legal, and product teams.
Step 3: Develop a Targeted Improvement Plan
For each priority dimension, identify concrete actions to advance to the next maturity level. For example:
If you're at Level 2 in "Identifying RAI Risks":
- Implement structured impact assessments for all AI projects
- Engage stakeholders to understand how risks affect them
- Develop a framework for prioritizing risks based on severity and likelihood
Remember, you don't need to reach Level 5 in every dimension. For many organizations, Level 3 or 4 may be sufficient depending on your AI use cases.
Step 4: Build Cross-Functional Governance
The RAI MM emphasizes collaboration as the core driver of maturity. This isn't just theoretical - it's practical necessity.
Effective RAI governance requires:
- A cross-functional steering committee with representation from security, data science, legal, and product
- Clear roles and responsibilities for RAI activities
- Regular review cycles to assess progress and adjust course
I've seen organizations create dedicated RAI teams that operate in isolation from security. This approach inevitably fails. Security leaders must be integral to RAI governance.
Step 5: Implement Continuous Monitoring
RAI isn't a one-time assessment - it's an ongoing process, so treat it as such. Establish mechanisms to continuously monitor your RAI posture:
- Regular reassessments of maturity levels
- Incident reviews that incorporate RAI considerations
- Feedback loops from AI system monitoring back to governance
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
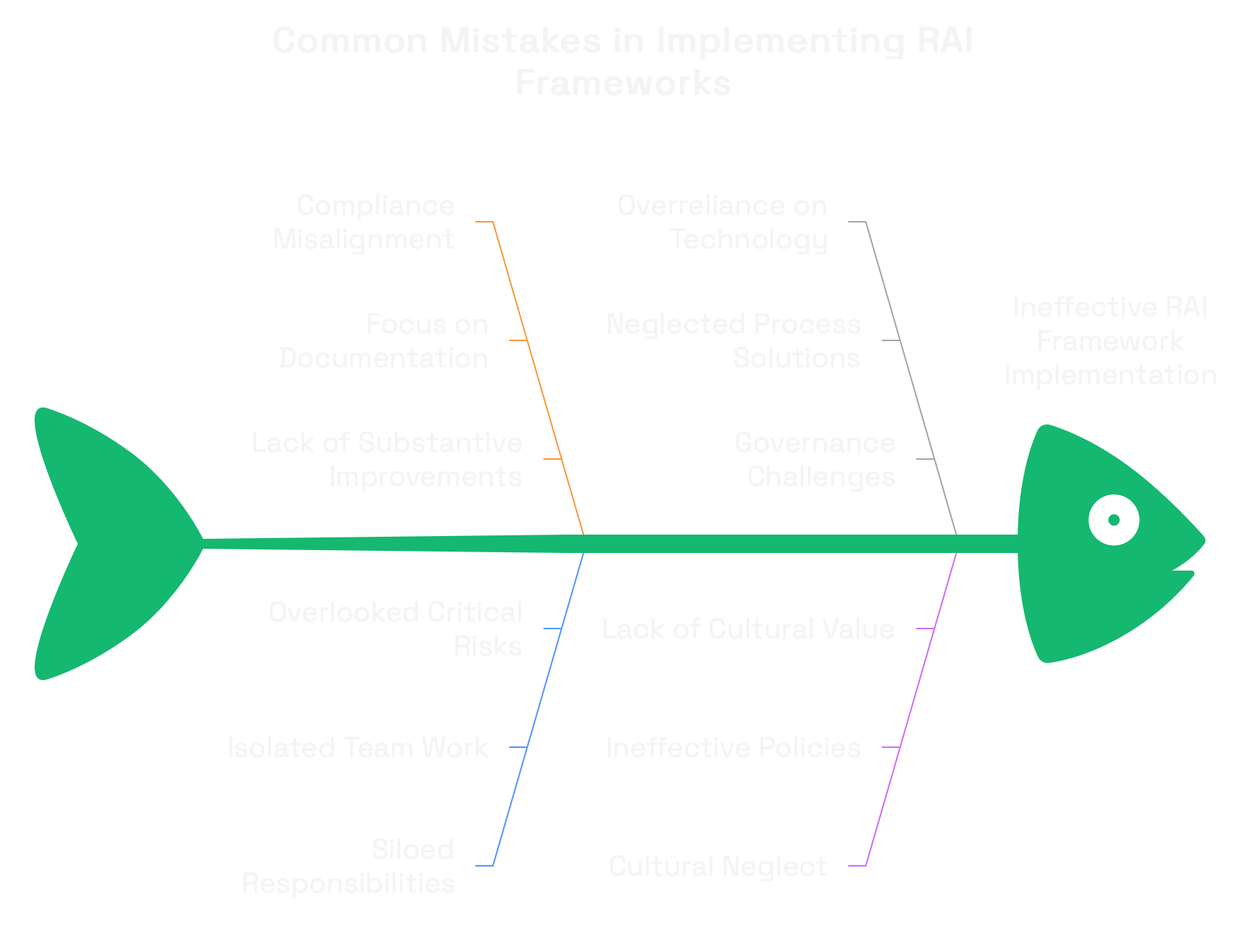
In implementing RAI frameworks, I've seen security leaders make several common mistakes:
- Treating RAI as a compliance exercise: RAI is about risk management, not checkbox compliance. Focus on substantive improvements, not documentation.
- Siloing RAI responsibilities: When security, data science, and legal teams work in isolation, critical risks fall through the cracks.
- Overemphasizing technical solutions: Many RAI challenges require process and governance solutions, not just technical controls.
- Neglecting cultural factors: Without a culture that values responsible AI, even the best policies and tools will be ineffective.
- Trying to boil the ocean: Attempting to reach Level 5 across all dimensions simultaneously will lead to burnout and failure. Prioritize and sequence your efforts.
The Security Leader's Roadmap to RAI Maturity
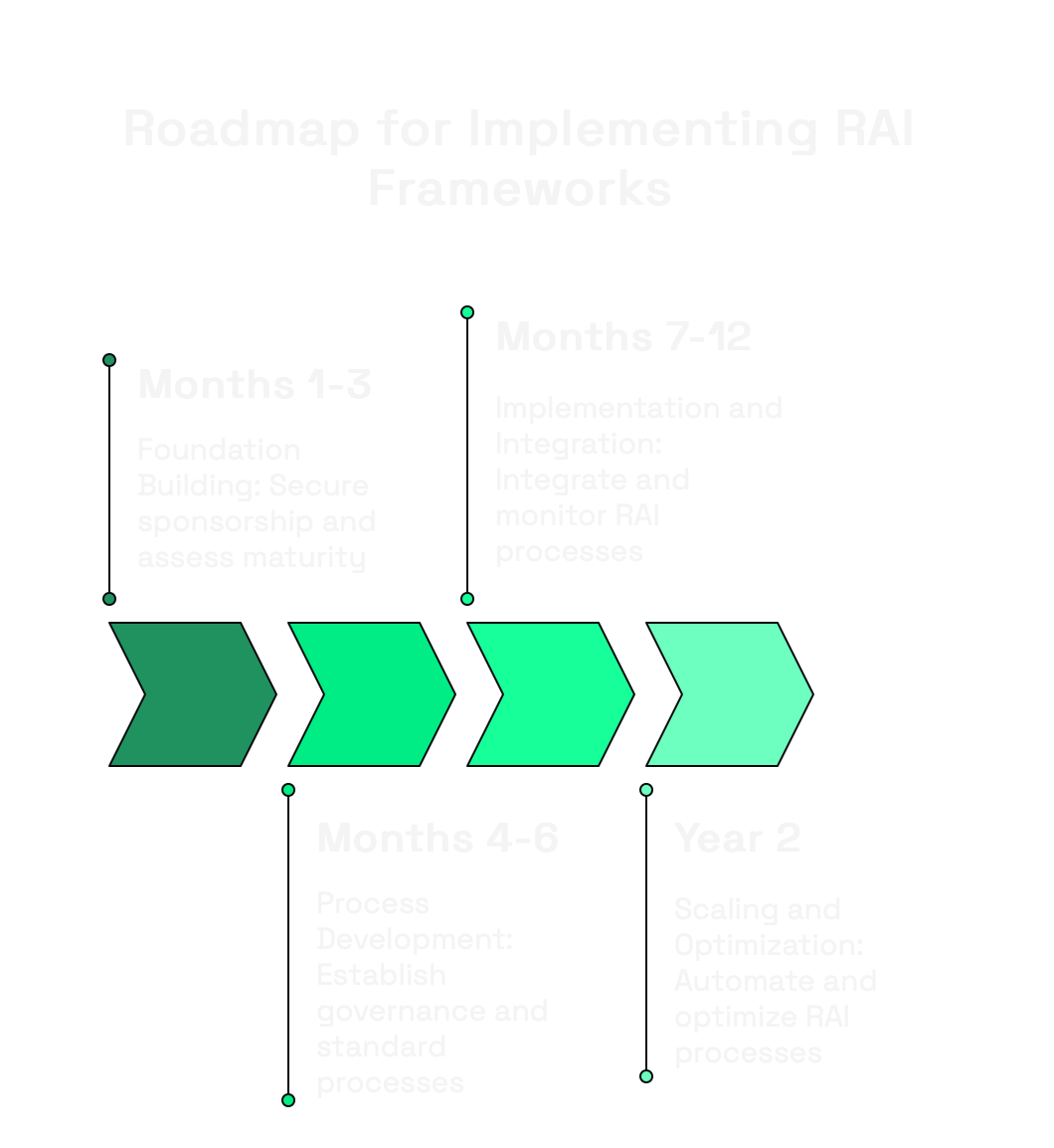
Now, lets have a look at a practical roadmap that you can offer to your ELT or SLT:
Months 1-3: Foundation Building
- Secure executive sponsorship for RAI initiatives
- Assess current maturity levels across all dimensions
- Develop a basic RAI policy aligned with your organization's values
- Identify key stakeholders across functions
Months 4-6: Process Development
- Establish a cross-functional RAI governance committee
- Develop standard processes for AI risk assessments
- Create documentation templates for transparency
- Begin training security teams on AI-specific risks
Months 7-12: Implementation and Integration
- Integrate RAI processes into existing security workflows
- Implement monitoring for AI-specific risks
- Develop metrics to track RAI maturity progress
- Create feedback mechanisms to continuously improve
Year 2: Scaling and Optimization
- Automate RAI processes where appropriate
- Develop advanced capabilities for AI risk monitoring
- Share lessons learned across the organization
- Contribute to industry RAI standards and practices
The Bottom Line for Security Leaders
The RAI Maturity Model isn't just another framework - it's a strategic tool that can help you navigate the complex intersection of AI and security.
By systematically assessing and improving your organization's RAI capabilities, you can:
- Reduce the risk of AI-related security incidents
- Build trust with customers and regulators
- Enable responsible innovation within your organization
- Position yourself as a strategic partner in AI governance
The organizations that thrive in the AI era won't be those with the most advanced models, but those that can deploy AI responsibly, securely, and ethically.
Play the long game!